您當前的位置:檢測資訊 > 科研開發
嘉峪檢測網 2021-06-17 09:53
受貽貝的粘附性能與關節軟骨的潤滑性能啟發,本研究采用無規共聚法合成了多巴胺-磷酰膽堿聚合物(DMA-MPC),并利用多巴胺輔助共沉積的方式在鈦合金(Ti6Al4V)表面構建了仿生自吸附聚合物涂層,獲得了兼具增強潤滑和抑菌粘附的材料,進而基于原子力顯微鏡(AFM)從微觀層面研究了細菌與涂層間的相互作用,提出了基于水合斥力的抑菌機理。
01研究內容簡介
醫用植入物在使用過程中面臨的關鍵挑戰之一是有限的表面潤滑和細菌生物膜的形成,這可能導致嚴重的組織損傷及一系列連續的并發癥。在以往的研究中,醫用植入物表面的潤滑性能和抑菌性能沒有得到很好的結合,并且大部分涂層材料的功能化過程較為復雜,也極大地影響了其臨床應用。因此,設計一種溫和的、新穎的表面功能化方法,同時考慮增強潤滑和抑菌粘附非常重要。
在人體健康的關節軟骨中,透明質酸、蛋白聚糖、潤滑素及磷脂等生物大分子組成的表面水合潤滑層是關節保持良好潤滑性能的重要原因,基于水合潤滑機理的磷酰膽堿類聚合物涂層也獲得了越來越多的關注;自然界中的貽貝可通過黏附蛋白牢固地附著在多種基體表面,多巴胺是粘附蛋白成分中最常見的衍生物,具有與其相似的粘附性質。受此啟發,本文設計、合成了修飾不同比例仿生自吸附聚合物涂層的Ti6Al4V@DMA-MPC,在進行潤滑特性篩選后,采用多巴胺輔助共沉積的方式進一步輔助涂層的構建。此外,分別在宏觀和微觀層面研究了涂層改善前后的抑制蛋白、細菌粘附的特性,利用AFM力曲線模式測定了親/疏水探針或者細菌與涂層之間的相互作用力,并分析了涂層的水合斥力抑菌機理,研究示意圖如下,Fig. 1.

Fig. 1. Illustration showing the facile fabrication of PDA/DMA-MPC biomimetic coating for (A) excellent lubrication property based on the hydration lubrication mechanism and (B1-C2) enhanced bacterial resistance property based on hydration repulsion: (B1) quantitative evaluation of dynamic adsorption of proteins on copolymer-coated Au-Ti sensors using QCM, (B2) qualitative evaluation of bacterial resistance of copolymer-coated Ti6Al4V substrate for 24 h, and force measurements probing possible interactions between biomimetic coating and (C1) hydrophobic tips or (C2) living bacteria on the nanoscale using AFM.
常規的材料學表征證明Ti6Al4V@DMA-MPC制備成功后,利用AMF接觸模式篩選出最優的比例進行后續研究。首先搭建了微流控通道,并構建了具有熒光特性的涂層基底進行流動實驗,通過熒光強度的變化來考察涂層的穩定性。同時,石英晶體微天平(QCM)實驗表明PDA/DMA-MPC涂層具有更優異的自吸附特性,并能獲得相對更厚、更柔性的涂層,Fig. 2.

Fig. 2. (A) XPS of four different Ti6Al4V substrates. (B) High-resolution narrow spectrum of N 1s for (B1) Ti6Al4V@PDA, (B2) Ti6Al4V@DMA-MPC and (B3) Ti6Al4V@PDA/DMA-MPC. (C) WCA and (D) surface morphologies of (C1, D1) Ti6Al4V, (C2, D2) Ti6Al4V@PDA, (C3, D3) Ti6Al4V@DMA-MPC (1:4) and (C4, D4) Ti6Al4V@PDA/DMA-MPC (1:4). The Ti6Al4V substrates were treated with plasma to obtain hydroxylated surfaces. (E) Frequency and dissipation changes associated with the self-adhesive biomimetic coating for (E1) DMA-MPC and (E2) PDA/DMA-MPC. (F) Quantitatively characterized the durability of the coating by monitoring the change of fluorescence intensity in microfluidic channel under scouring experiments. The fluorescence graphs in different scouring time: (F1) 0 h, (F2) 7 h, (F3) 1 d and (F4) 3 d. (F5) The changes of fluorescence intensity in different scouring time.
在Au-Ti芯片傳感器上利用QCM實時定量評價了涂層改善前后對蛋白的動態吸附性能,結果表明PDA/DMA-MPC涂層具有優異的抑制蛋白粘附性能。通過掃描電鏡(SEM)觀察涂層改善前后大腸桿菌的粘附情況,與細菌共培養24 h后發現,在涂層表面僅有少量粘附,表明涂層能夠有效地抵抗細菌的初始粘附;與細菌共培養8 d后的定量細菌涂布實驗結果表明,涂層組的抑菌效果顯著,PDA/DMA-MPC涂層的抑菌率達到98%,Fig. 3.

Fig. 3. (A) Frequency and dissipation changes associated with dynamic adsorption of BSA on bare and copolymer-coated Au-Ti sensors. (B) The bacterial resistance adhesion property tested by spread plate assay. (B1) The bacterial resistance ratio of different substrates. The colony pictures of (B2) bare Ti6Al4V, (B3) Ti6Al4V@DMA-MPC and (B4) Ti6Al4V@PDA/DMA-MPC, and the bacterial counts are 100 %, 17.5 % and 1.9 %, respectively. (C) Representative SEM images showing E. coli adhesion on the Ti6Al4V substrates after cultured for 24 h: (C1) bare Ti6Al4V, (C2) Ti6Al4V@DMA-MPC and (C3) Ti6Al4V@PDA/DMA-MPC.
最后,利用AFM測試了親/疏水兩種探針與涂層基底之間的相互作用力,發現疏水探針與PDA/DMA-MPC涂層在相互接近的過程中具有更強、更長程的排斥力,這說明涂層可能會在阻止蛋白質類成分的初始粘附方面發揮重要的排斥功能;同樣地,PDA/DMA-MPC涂層修飾的探針與大腸桿菌基底在相互接近的過程中能夠產生最強、最長程的斥力,同時在停留不同時間后,在分離過程中能夠產生最小、最短程的粘附力,以上結果說明涂層優異的水合斥力屏障作用能夠顯著提高抑菌粘附性能,Fig. 4.
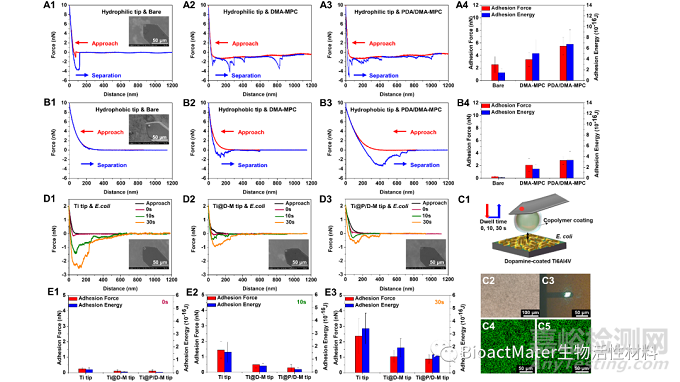
Fig. 4. Representative force-distance curves during approach and separation process in the force measurements using AFM for (A1-A3) hydrophilic tip and (B1-B3) hydrophobic tip against the bare Ti6Al4V, Ti6Al4V@DMA-MPC and Ti6Al4V@PDA/DMA-MPC substrates. The inset figures are the SEM images of the tips. (A4, B4) Statistical analysis of adhesion force and adhesion energy obtained from the separation process. (C1) Schematic illustration showing the force measurements between copolymer-coated AFM tip against bacteria-coated substrate, with different dwell times of 0 s, 10 s and 30 s. (C2) Microscopy images of the bacteria-coated substrate. (C3) Microscopy images in the force measurements between AFM tip and bacteria-coated substrate. The green fluorescence indicates that the immobilized bacteria are alive (C4) before and (C5) after the force measurements. (D) Representative force-distance curves during approach and separation process in the force measurements for (D1) Ti tip, (D2) Ti@D-M tip and (D3) Ti@P/D-M tip against bacteria-coated substrates. (E) The adhesion force and adhesion energy between three different AFM tips and bacteria-coated substrates obtained from the separation process under the dwell time of (E1) 0 s, (E2) 10 s and (E3) 30 s.
02論文第一/通訊作者簡介
通訊作者:張洪玉
清華大學機械工程系摩擦學國家重點實驗室副研究員,從事生物摩擦學研究,設計并研發了多種生物醫用潤滑材料與技術,包括微納米顆粒、聚合物涂層以及納米纖維膜等,用于骨關節損傷修復、醫療器械表面改性、組織粘連預防與修復等方面,承擔國家自然科學基金優秀青年基金等項目10余項,以第一或通訊作者在Adv. Funct. Mater., Nano Lett., Biomaterials, Small, Nano Energy等期刊發表SCI收錄論文50余篇(其中封面論文5篇),以第一發明人獲授權國家發明專利10余件,參與撰寫中英文專著4本,擔任JWKJW生物及交叉技術領域先進仿生系統專家組助理等職務。
03資助信息
本研究得到了國家自然科學基金(52022043)、清華大學精準醫學科研計劃(10001020120)以及首都衛生發展科研專項(2020-2Z-40810)等項目的資助。
04原文信息
Ying Han#, Weiwei Zhao#, Yiwei Zheng, Haimang Wang, Yulong Sun, Yifei Zhang, Jing Luo, Hongyu Zhang*.
Self-adhesive lubricated coating for enhanced bacterial resistance.
Bioactive Materials 6 (2021) 2535-2545.

來源:BioactMater生物活性材料


